At Brown Pharmaceutical, we understand that the quality of medical equipment directly impacts patient care and safety. As a leading supplier in the healthcare industry, we are dedicated to providing top-of-the-line medical equipment and solutions to support healthcare professionals and institutions in delivering exceptional care.
Immunochromatographic Reader
An immunochromatographic reader is a device used to interpret the results of immunochromatographic tests, which are commonly employed for diagnostic purposes. These tests are often used for detecting specific substances, such as pathogens or biomarkers, in a sample, like blood or urine.
1. Test Principle: Immunochromatographic tests, also known as lateral flow assays, use a paper-based format where a sample is applied to one end of a test strip. The sample moves along the strip through capillary action and interacts with various reagents, including antibodies or antigens. This interaction produces a visual signal, often in the form of colored lines.
2. Function of the Reader: The immunochromatographic reader is designed to quantitatively and qualitatively analyze the results of these tests. It typically works by shining a light through the test strip and measuring the intensity of the color or the presence of lines. This data is then processed to give a clear result, often displayed digitally.

3. Advantages: Using a reader can improve the accuracy and consistency of test results compared to visual interpretation. It reduces the potential for human error and can provide more objective and reproducible results.
4. Applications: These readers are used in various fields, including medical diagnostics (e.g., pregnancy tests, disease detection), environmental monitoring, and food safety testing.
The BPL M-Rad 3.5 DR
Is a digital radiography (DR) system used in medical imaging. Here is a summary of its key features and functions:
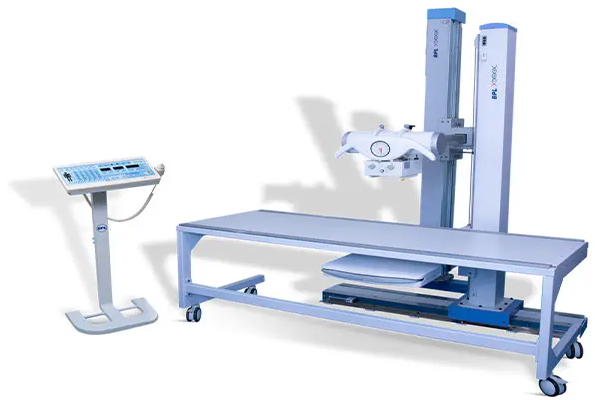

- Digital Radiography: The M-Rad 3.5 DR is a type of digital radiography system, which means it captures X-ray images digitally rather than using traditional film. This allows for quicker image acquisition, enhanced image quality, and easier storage and sharing of images.
- Features:
- High Resolution: It provides high-resolution images, which are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
- Efficient Workflow: The system is designed to streamline the workflow in radiology departments, offering features such as automated image processing and fast image retrieval.
- Image Quality: The digital system often includes advanced imaging technology to enhance image clarity and contrast.
- Applications: It is used for a wide range of diagnostic imaging applications, including examinations of the chest, abdomen, bones, and other body parts. It's beneficial in various clinical settings, including hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic imaging centers.
- User Interface: Modern DR systems like the M-Rad 3.5 DR usually come with user-friendly interfaces that facilitate easy operation and integration with hospital information systems (HIS) and picture archiving and communication systems (PACS).
- Advantages:
- Speed: Faster image acquisition and processing compared to traditional film-based systems.
- Reduced Radiation: Digital systems often require less radiation to produce diagnostic-quality images.
- Image Storage and Sharing: Digital images can be easily stored, retrieved, and shared electronically.
SubCyclo
SubCyclo is a device used in medical diagnostics and specifically in the field of immunoassays, particularly for analyzing low concentrations of analytes. It’s typically used in various clinical and research applications for detecting and quantifying substances in biological samples.
- High Sensitivity: SubCyclo is designed to detect very low levels of analytes, making it useful for assays that require high sensitivity.
- Advanced Technology: It often incorporates sophisticated optical or electronic detection methods to achieve its high sensitivity.
- Versatility: Used in various types of immunoassays, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), lateral flow assays, and other diagnostic formats.

Applications:
- Clinical Diagnostics: It can be employed to measure biomarkers, hormones, and other substances at very low concentrations, which is crucial for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of diseases.
- Research: In research settings, it helps in the analysis of low-abundance proteins, cytokines, and other molecules of interest.
Advantages:
- Precision: Offers precise measurement capabilities, crucial for accurate diagnostics and research outcomes.
- Efficiency: Can improve the efficiency of testing by providing rapid and reliable results for low-concentration targets.
- Reduced Sample Volume: Often requires smaller volumes of sample compared to other methods, which can be advantageous when dealing with limited or precious samples.